1. Introduction
Vi comes preinstalled in most Linux/Unix operating systems. Most commonly used to edit programs or configurations file in Linux. If you look for more advanced features you can use VIM which is a vi-like editor.
In this tutorial, we learn about vi / vim text editor and some of its useful commands.
2. Vi Modes
The vi editor in theory has only two modes: Command mode and Insert Mode. But practical you have two more modes.
1. Command (normal) mode
When you open vi editor it starts in Command mode. In this mode, the editor accepts commands but won't display on the screen. Commonly used to navigate, edit and search content. Press ESC key to enter into Command mode from other modes. Most vi commands are entered from this mode.
2. Insert Mode (input mode)
Insert mode is used to edit or insert text to the file as would do in a regular text editor. Press the letter i from the keyboard to enter Insert mode.
3. Escape mode
You can change to escape mode from command mode only. Press : (colon) key from the keyboard to enter Escape mode. This mode is commonly used to make actions on the file such as save, quit and theme selection, etc.
4. Visual mode
Visual mode is used for selecting blocks of text in the file. Once selected can take actions on it such as copy and cut. To enter character-wise visual mode press 'v' and for line-wise visual mode press 'Shift +v'.
3. Opening and Saving Files
Open vi editor
The best way to open vi editor type vi filename from the command line.
vi text1.txtThis opens the existing file named text1.txt and if text1.txt doesn't exist then it creates a new file.
Let's check here how to create a new file name file1.txt:
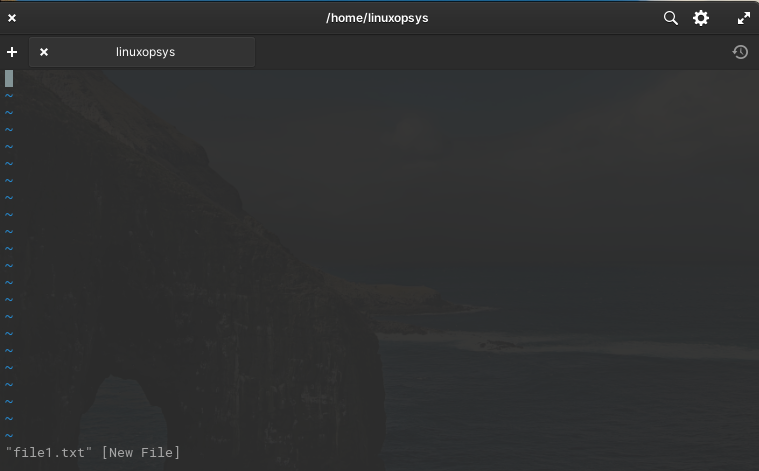
The symbol '~' indicates unused lines.
Press 'i' from the keyboard to enter Insert mode.
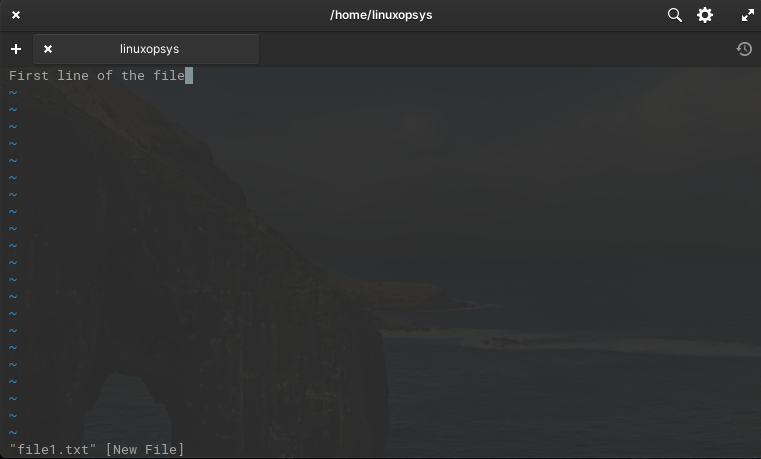
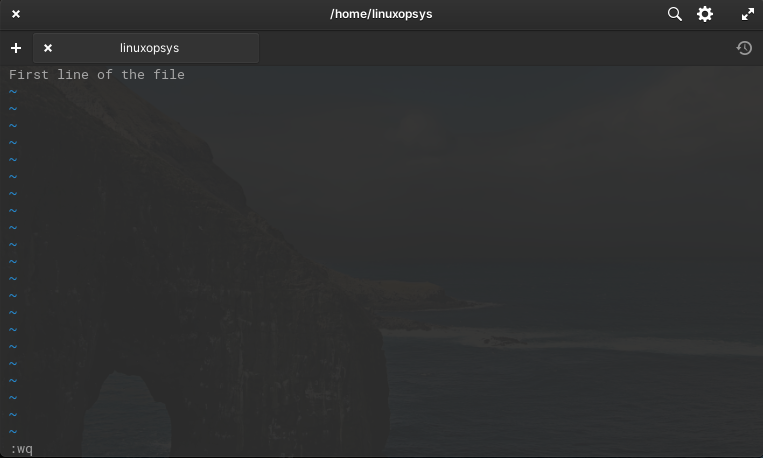
Press Esc key and then type :wq to save & quit. You can now view the file content using the cat or using vi command itself.
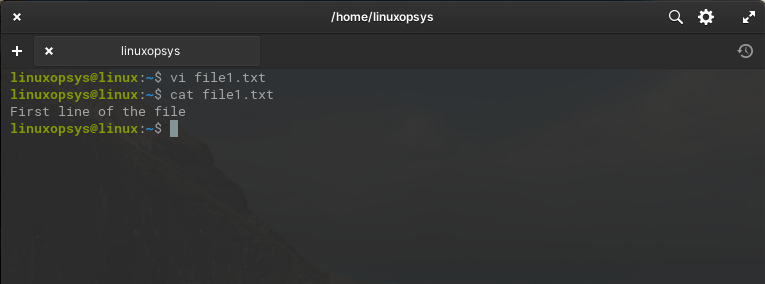
Note: If the file is read-only or you don't have permission to write to it, you'll receive an error message and won't be able to save and quit.
Exit (quit) vi editor without saving
To exit vi editor without saving the file content go through the following steps:
1. Press Escape key from your keyboard to enter command mode
2. Press : (colon) key from your keyword, now you will see a colon prompt followed by a flashing cursor at the lower-left corner of the screen.
3. Type the command q! and press Enter key. This will close the vi editor and all changes you made will not be saved.
Exit (quit) vi editor with saving (forcefully)
1. Press Escape key from your keyboard to enter command mode
2. Press : (colon) key from your keyword, now you will see a colon prompt followed by a flashing cursor at the lower-left corner of the screen.
3. Type the command wq! and press Enter key. This command is similar to :wq, but it forces the write and quit operation even if there are unsaved changes or if the file is read-only.
4. Useful Vi Shorcuts
4.1. Navigation
The commonly used vi navigations are line, screen, and word.
Line Navigation
Let's check the navigation shortcut to move within a line:
- Move cursor to the beginning of the current line: '0' (zero)
- Move cursor to the end of the current line: '$' (dollar sign)
- Move cursor to the first non-blank character of the current line: '^'
- Move cursor to the top line of the file: 'gg'
- Move cursor to the last line of the file: 'G'. For example to move to line 20, type '20G'.
Screen Navigation
- Move cursor to the first line of the current screen: 'H'
- Move cursor to the middle of the current screen: 'M'
- Move cursor to the bottom of the current screen:: 'L'
- Move cursor one full screen forward: 'Ctrl + F'
- Move cursor one full screen backward: 'Ctrl + B'
Word Navigation
- Move cursor to the end of current word: 'e'
- Move cursor to the beginning of current word: 'b'
- Move cursor to the beginning of next word: 'w'
4.2. Editing, Copying, Cutting, and Pasting
Delete Operation
Enter the command mode by pressing 'Esc' key:
- Delete the character on which has the cursor: 'x'
- Delete the line which has the cursor: 'dd. For example, to delete four lines starting from the current cursor position type '4dd'.
Select and Cut
- Enter visual mode (v), select the text, then press d
Select and Copy
- Enter visual mode (v), select the text, then press y
Paste
- Press p to paste after the cursor or P to paste before the cursor. To perform undo Press 'u'
4.3. Searching
Search forward for a pattern
- /<pattern> - Press / followed by the pattern, then press Enter. Use n or * to find the next occurrence. Use # to move the cursor to the previous occurrence of the current word.
Search backward for a pattern
- ?<pattern> - Press ? followed by the pattern, then press Enter. Use n to find the previous occurrence.
Searching and Replacing
- To replace the current occurrence of the search pattern, type :s/old/new/. Replace old with the pattern you want to replace, and new with the replacement text. For example, to replace the word "tom" with "bob", type :s/tom/bob/.
- To replace all occurrences of the search pattern in the current line, use :s/old/new/g. The g at the end stands for "global" and replaces all occurrences in the line.
- To replace all occurrences in the entire file, use :%s/old/new/g. The % represents the whole file.
- To confirm each replacement interactively, use :%s/old/new/gc. The c at the end stands for "confirm".
Miscellaneous Commands
To display line number in the file type :set number and to hide it use :set nonumber
To Display vi/vim color scheme type :colorscheme [space] [crtl+d]. And to set a specific color scheme :colorscheme darkblue
Display the line number of the current line in the prompt type :.=



Comments