adduser command is used to create a new user in Linux. It is a front-end tool that simplifies the low-level useradd command. It is more user-friendly and interactive. In the backend, it uses a Perl script to provide a nice interactive high-level tool. It uses the configuration information in /etc/adduser.conf to perform actions.
Basic Syntax
adduser [options] usernameCommon options are:
-b,--base-dir BASE_DIR: Set default base directory.-c,--comment COMMENT: Add user's description (typically full name).-d,--home HOME_DIR: Set user's home directory.-D: Allows you to view or modify default values used when creating new user accounts. Supported options to use with -D are--base-dir BASE_DIR,---expiredate EXPIRE_DATE,--inactive INACTIVE,--gid GROUP,--shell SHELL.-e,--expiredate EXPIRE_DATE: Set account expiration date.-f,--inactive INACTIVE: Set days after password expiry until account disablement.-g,--gid GROUP: Set user's primary group.-G,--groups GROUP1[,GROUP2,...[,GROUPN]]]: Add user to additional groups.-k,--skel SKEL_DIR: Set skeleton directory for user's home.-K,--key KEY=VALUE: Override default values.-m,--create-home: Create user's home directory.-M: Do not create user's home directory.-N,--no-user-group: Skip creating group with the same name as user.-o,--non-unique: Allow non-unique user IDs.-p,--password PASSWORD: Set user's password (not recommended).-r,--system: Create a system account.-s,--shell SHELL: Set user's login shell.-u,--uid UID: Set user's numerical ID.-U,--user-group: Create group with the same name as user.-Z,--selinux-user SEUSER: Set SELinux user.
Remember some options are specific to Distros. For example -D option is not supported on Debian-based distros.
Using adduser Command
Let's look into some of the most common use cases of the adduser command.
1. Add a new normal user
By default, adduser command adds a normal user to the system. To add a new user simply type adduser followed by the name of the user.
Syntax:
adduser [username]For example to add a normal user with name bob, type:
sudo adduser bob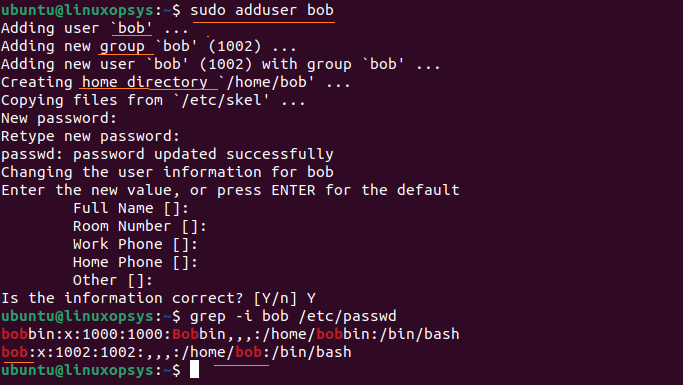
adduser command does the following by default when adding a new user:
- Creates a user using the username provided. Choose the first available UID from the range specified in the configuration file.
- Creates a group having the same name as the user. Choose available GID.
- Adds user to the group created.
- Creates a home directory for the user (/home/<username>).
- Starts passwd command to set up the user's password.
- Asks for additional user details.
To add an organizational user account ie system account use --system option. The difference between a normal user is it has no expiry date and uid is below 999.
2. Add a user with a different home directory
By default adduser command creates user's home directory under /home. You can add --home or -d option to create a new user account with a different directory.
Syntax:
adduser [username] --home [directory-path]For example to create a user named tom with home directory /mnt/data/tom, type:
sudo adduser tom --home /mnt/data/tom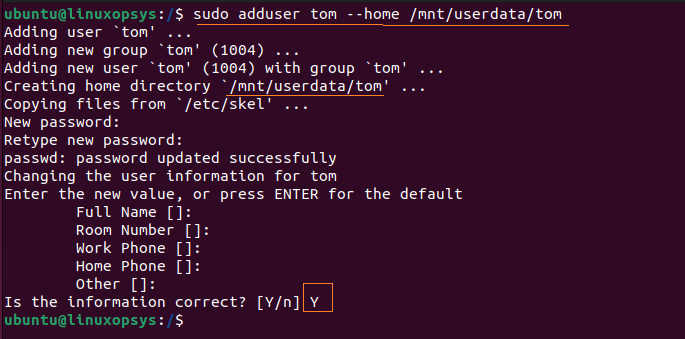
3. Adding a new user to a group
Using adduser command you can easily add an existing user to an existing group.
Syntax:
sudo adduser [existing-username] [exiting-group-name]For example to add a user named john to the group named developers, type:
sudo adduser tom developers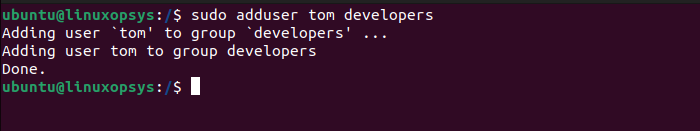
Make sure the user name and group already exist in the system.
4. Add a User with no password
The adduser with --disabled-login allows to you to add a user with no password. Until the password is set the user won't be able to login.
Syntax:
sudo adduser --disabled-login [username]For example to add a user named bobs with no password, type:
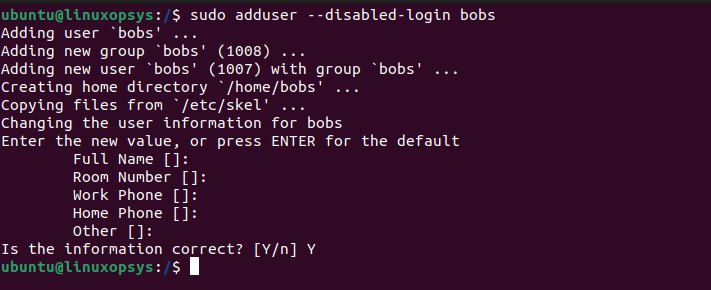
This command doesn't prompt for a password. Later if you want the user to login, create a password using passwd command.
5. Add a user with disabled password
The adduser command with --disabled-password option allows you to add a user account with no password. But the user can still possible to login the system using SSH keys.
Syntax:
sudo adduser --disabled-password [username]For example to add a user named john with no password, type:
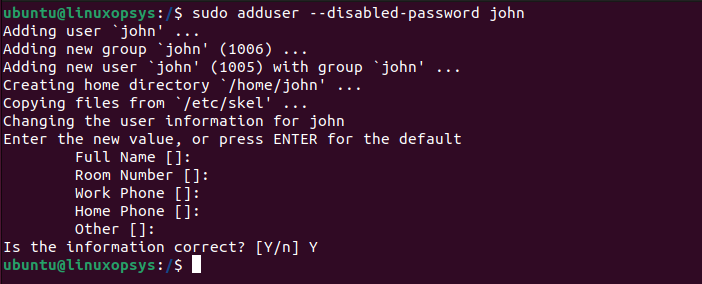
This is useful when you need a user with only ssh key login for secure authentication.
You can use --gecos option with empty string to avoid asking for finger information such as Full Name, Room Number, Work Phone, Home Phone, and Other. Example:
sudo adduser --disabled-password --gecos "" bob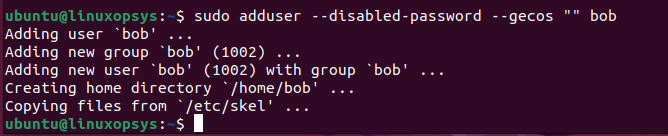
6. Use a different config file
Instead of using the default configuration file, we can instruct adduser command to use a custom config file. Use adduser command with --conf option for this.
Syntax:
sudo adduser [username] --conf [custom-config.conf]Example:
sudo adduser thomas --conf custom-config.conf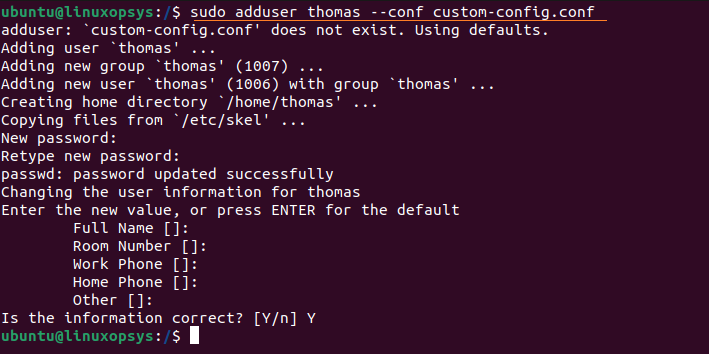
7. Add a user with a different shell
Instead of the default shell, you can manually specify the users login shell using --shell option. The default shell is specified in the /etc/adduser.conf configuration file - normally /bin/bash or /bin/sh is used.
You can use cat /etc/shells to list all your available shells in your Linux system. From the list choose your desired shell.
For example, to add a user named tomas with login shell zsh, type:
sudo adduser tomas --shell /bin/zsh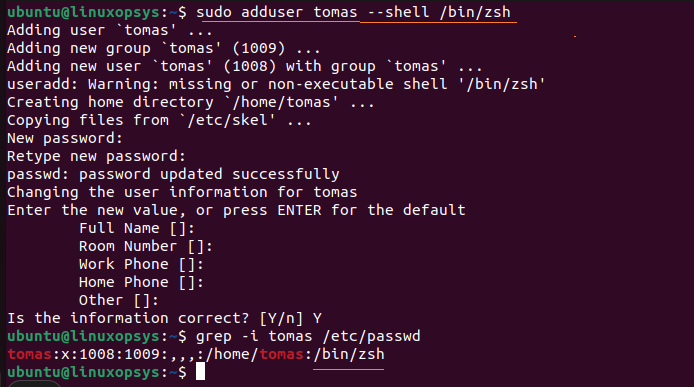
You can verify the login shell of the user by listing passwd file as follows:
grep -i tomas /etc/passwd



Comments