The cd command in short is "change directory". It's used to navigate from one directory to another within the filesystem. When working in a command-line interface or terminal, the cd command allows users to move around the different folders/directories of the system.
Syntax
Basic syntax of cd command:
cd [directory_name]While the command itself doesn’t have many options, understanding its structure is vital.
To navigate into a directory using the cd command in Linux or Unix-like systems, a user needs the execute (x) permission on that directory. To list its contents should require read (r) permission. The combination r-x for a directory is common as it allows a user to navigate into the directory and list its contents.
Common Usage
Let's look into the very common usage of cd command:
Navigating into a directory:
To navigate into a specific directory, you use the cd command followed by the name or path of the directory you want to enter.
cd /path/to/directory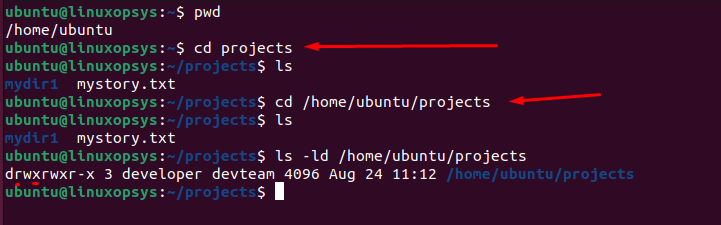
Using pwd immediately after cd is a good habit, especially when working in a terminal without any visual indicators of the current directory. It ensures you're in the correct directory before performing operations like file creation, deletion, or modification.
Using an absolute path - If you know the full path to the directory you want to navigate to, you can provide the entire path, starting from the root /.
Using a Relative Path - If the target directory is a child of your current directory, you can simply provide its name. Example: cd Documents
When you navigate to the directory error message "No such file or directory" is usually, a typo or a wrong path is the culprit. The system will throw a "Permission denied" message if a regular user trying to access restricted directories such as /etc, /root, /var, /boot, etc - you should have administrative rights.
Note: When you start typing the name of a directory and press the Tab key, the shell will attempt to autocomplete the directory name based on existing directories that match the prefix you've typed. If there are multiple matches, pressing Tab twice will display all possible completions.
Going back to the home directory:
Simply typing cd and pressing enter will take you to your home directory.
cd
Alternatively can use the tilde (~) that represents the home directory of the current user. Therefore, you can use it with the cd command to navigate to the home directory.
cd ~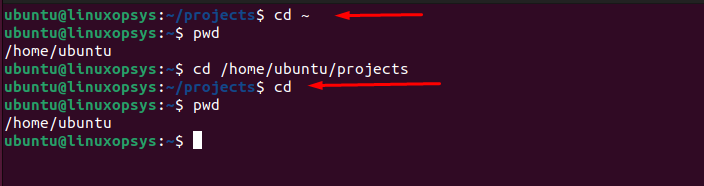
After executing either of these commands, you'll be located in your home directory, which is typically something like /home/username for regular users or /root for the root user.
Moving up one directory:
You use the cd command followed by ... The .. symbol represents the parent directory of the current directory.
cd ..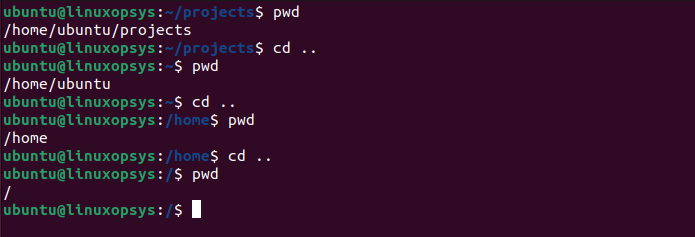
After executing this command, you'll be in the parent directory of your previous location. If you keep using cd .. repeatedly, you will eventually reach the root directory /, which is the topmost level in the filesystem hierarchy.
The cd../ functionally does the same thing as cd .. command. Using the trailing slash becomes particularly relevant when specifying further directories. For instance, if you're in /home/user/Documents and you want to navigate to /home/user/Pictures, you could use: cd ../Pictures. This is more intuitive when chaining directory names in a path. With that note, to navigate up two levels in the directory structure use cd ../../.
Returning to the previous directory:
To return to the previous directory in a Linux or Unix-like system, you can use the cd command with the - (dash) option.
cd -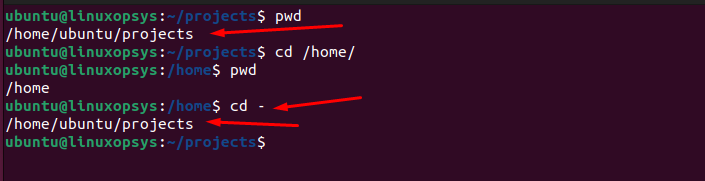
When you execute this command, the shell will take you back to the directory you were in before the last cd command. The system will also display the path of that directory as output, letting you know where you've navigated to.
Heading to the root directory:
Use the cd command followed by a forward slash /.
cd /
After executing this command, you'll be located in the root directory, and any commands you execute will operate from this directory context unless otherwise specified. If you've ever lost within the directory structure, you can quickly get back to the root directory by typing cd /. From there, you can navigate to any other location in the filesystem with relative ease.



Comments