Often, there is a need to enable or disable services temporarily or permanently on our Ubuntu system. Sometimes, we may require certain services to start up automatically on boot up e.g ssh or web servers and sometimes we may need to disable services we no longer require and are hogging the CPU and RAM.
In this guide, we take a look at how we can enable and disable services on Ubuntu. To do this, we must first understand that there are 3 main init systems for Ubuntu
- Systemd
- Upstart
- SysV
Each init system has a different way of starting and stopping services. We'll take a look at each one of these.
How to enable and disable services in Systemd init
To start a service in systemd run the command as shown:
systemctl start service-nameFor example, to start apache web service, run
systemctl start apache2To verify that the service is running, run
systemctl status apache2Output
● apache2.service - LSB: Apache2 web server
Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/apache2; bad; vendor preset: enabled)
Drop-In: /lib/systemd/system/apache2.service.d
└─apache2-systemd.conf
Active: active (running) since Thu 2018-03-15 17:09:05 UTC; 35s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
CGroup: /system.slice/apache2.service
├─2499 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
├─2502 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
└─2503 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
Mar 15 17:09:04 ip-172-31-41-251 systemd[1]: Starting LSB: Apache2 web server...
Mar 15 17:09:04 ip-172-31-41-251 apache2[2475]: * Starting Apache httpd web ser
Mar 15 17:09:05 ip-172-31-41-251 apache2[2475]: *
Mar 15 17:09:05 ip-172-31-41-251 systemd[1]: Started LSB: Apache2 web server.
To stop the service running service
systemctl stop apache2To confirm that the service is not running, run
systemctl status apache2Output
● apache2.service - LSB: Apache2 web server
Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/apache2; bad; vendor preset: enabled)
Drop-In: /lib/systemd/system/apache2.service.d
└─apache2-systemd.conf
Active: inactive (dead) since Thu 2018-03-15 17:19:47 UTC; 12s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
Process: 2822 ExecStop=/etc/init.d/apache2 stop (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS
Process: 2687 ExecStart=/etc/init.d/apache2 start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCE
Mar 15 17:10:11 ip-172-31-41-251 systemd[1]: Starting LSB: Apache2 web server...
Mar 15 17:10:11 ip-172-31-41-251 apache2[2687]: * Starting Apache httpd web ser
Mar 15 17:10:12 ip-172-31-41-251 apache2[2687]: *
Mar 15 17:10:12 ip-172-31-41-251 systemd[1]: Started LSB: Apache2 web server.
Mar 15 17:19:46 ip-172-31-41-251 systemd[1]: Stopping LSB: Apache2 web server...
Mar 15 17:19:46 ip-172-31-41-251 apache2[2822]: * Stopping Apache httpd web ser
Mar 15 17:19:47 ip-172-31-41-251 apache2[2822]: *
Mar 15 17:19:47 ip-172-31-41-251 systemd[1]: Stopped LSB: Apache2 web server.
To enable apache2 service on boot up run
systemctl enable apache2To disable apache2 service on boot up run
systemctl disable apache2To restart the service
systemctl restart apache2To check whether the service is currently configured to start on the next boot up
systemctl is-enabled apache2Output
Executing /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install is-enabled apache2
enabled
To check whether the service is active
systemctl is-active apache2Output:
activeHow to remove Systemd services completely
What if you installed a package, and later on decide that you don't need it anymore. How do you go about removing it completely? Follow the commands below.
First, stop the service
systemctl stop service-nameThen disable the service
systemctl disable service-nameRemoving the service in systemd
rm /etc/systemd/system/service-namerm /etc/systemd/system/service-name/[related symlinks]Reload systemd
systemctl daemon-reloadFinally run,
systemctl reset-failedHow to enable and disable services in Upstart init
Upstart init system was unveiled just before systemd It was used in Ubuntu 9.10 to Ubuntu 14.10. It was later phased out paving way for systemd init in Ubuntu 15.04 and newer versions. In this example, let's see how we can start and stop, enable and disable services in Ubuntu 14.04.
Upstart makes use of config files for controlling services. These files are held under the /etc/init directory. These files are made up of plain text sections organized in stanzas and each stanza describes a service and how it works.
To check whether a service is running or not run the command below
initctl status service-nameOR
service service-name statusOR
status service-nameIn this example, we'll check the status of cups, a Linux print server.
initctl status cupsOR
service cups statusOR
status cupsOutput:
cups start/running, process 3029To stop the service run the command below
initctl stop cupsOR
service cups stopOR
stop cupsOutput
cups stop/waitingTo enable a service in Upstart init
In /etc/init/*.conf file, you'll find the "respawn" directive which jump-starts a service should it crash unexpectedly or should the system reboot. Its normally enabled by default.
For example , in /etc/init/cups.conf file below,
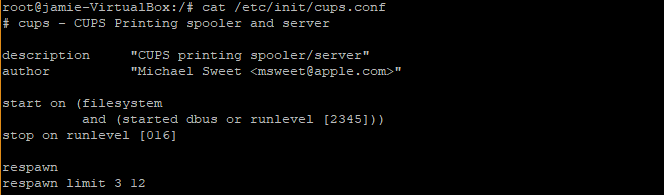
The first argument (3) is the number of attempts it will try to restart and the second argument (12) is the time interval between retries. If it fails to restart automictically. it will be kept in a stopped state.
To disable a service in upstart init
Run the command below:
echo manual >> /etc/init/service.overrideThis creates an override file that disables a service without altering the job definition at all.
For cups service, the command will be
echo manual >> /etc/init/cups.overrideUpon a reboot of the system, cups will be in a stopped state. If you wish to re-enable the service, you must delete the /etc/init/cups.override file.
Sysv-rc-conf tool
This is a text-based console that gives you an overview of different services and runlevels they are scheduled to start. It can be installed using the following command:
apt-get install sysv-rc-confTo execute the tool, run
sysv-rc-conf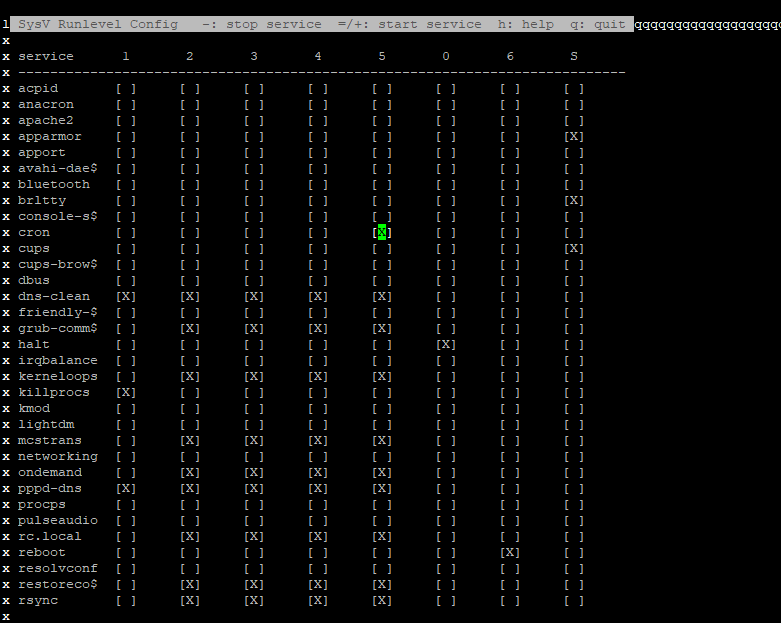
Jobs-Admin tool
This is another feature that allows you to control services and processes in a GUI environment. You can install this by running.
apt-get install jobs-admin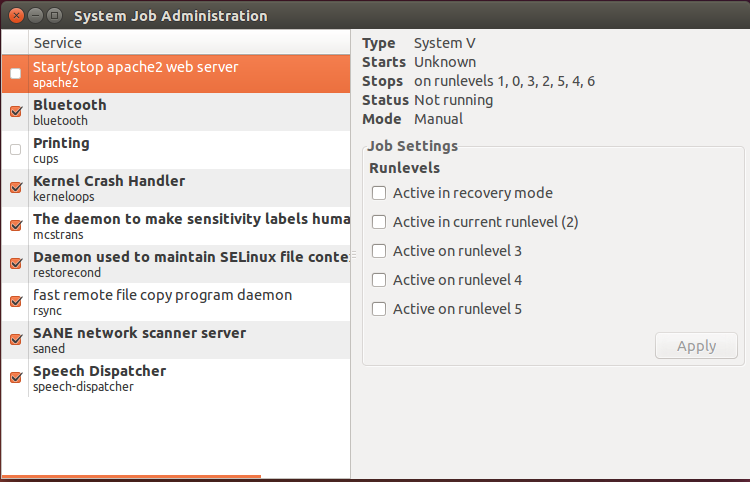
How to enable and disable services in SysV init
To enable a service in SysV init run
update-rc.d enable service-nameFor instance, If you want to enable apache web server, you would run
update-rc.d enable apache2To disable a service, run
update-rc.d disable service-nameFor example:
update-rc.d disable apache2Conclusion
Nearly all Linux systems run on Systemd init such as Ubuntu, Debian, RHEL, and CentOS Stream. You'll, therefore, discover that you'll be using more of the systemctl command to start, stop, enable and disable services. We welcome you to try out the commands as shown in this guide. Thank you.



Comments