Install a specific version of a package can be useful to avoid the bugs when you know which version of a package is concerned. Then make sure to disable a specific package from updating by holding the packages so it won't get automatically updated when you run 'apt-get upgrade'.
To handle Debian-based system packages, we use the apt-get command. To run this command you require administrative rights or a user with sudo privilege.
In this tutorial, we learn how to install a specific version of a package on Ubuntu.
1. Check the available versions of packages
Sometimes you can face issues or bug with a version of a package, this may cause you to choose a version which doesn't encounter bugs. Before installing, it is possible to check the available versions of a package with the apt-cache madison command. The syntax is
apt-cache madison packageYou can see the output below
$ apt-cache madison virtualbox
virtualbox | 5.0.40-dfsg-0ubuntu1.16.04.2 | http://cm.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-updates/multiverse amd64 Packages
virtualbox | 5.0.18-dfsg-2build1 | http://cm.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial/multiverse amd64 PackagesYou can also use the syntax command below
apt-cache policy packagejust as below
$ apt-cache policy virtualbox
virtualbox:
Installed: (none)
Candidate: 5.0.40-dfsg-0ubuntu1.16.04.2
Version table:
5.0.40-dfsg-0ubuntu1.16.04.2 500
500 http://cm.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-updates/multiverse amd64 Packages
5.0.18-dfsg-2build1 500
500 http://cm.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial/multiverse amd64 PackagesThen, with one of the two commands, you can decide to check the available version of a package with the releases versions on the official site or on the official GitHub.
2. Install a specific version of a package
When you have listed the versions to choose the specific one, you can install it with the apt-get install command followed by the name and the version of the package. So, you need to follow the syntax as below:
apt install package=version -VThe -V parameter helps to have more details about the installation
Practically, you can do as below:
sudo apt install virtualbox=5.0.18-dfsg-2build1 -V
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following additional packages will be installed:
dkms (2.2.0.3-2ubuntu11.5)
libgsoap8 (2.8.28-1)
libqt4-opengl (4:4.8.7+dfsg-5ubuntu2)
libsdl1.2debian (1.2.15+dfsg1-3)
libvncserver1 (0.9.10+dfsg-3ubuntu0.16.04.1)
virtualbox-dkms (5.0.40-dfsg-0ubuntu1.16.04.2)
....................
....................a. Simulate the installation
For some reason, you could need to make sure that the installation will not encounter any problem. To do that, it is possible to simulate the installation with the -s parameter respecting the syntax
sudo apt install -s packageFor example to install a specific version of virtualbox version 5.0.18-dfsg-2build1, type:
sudo apt install -s virtualbox=5.0.18-dfsg-2build1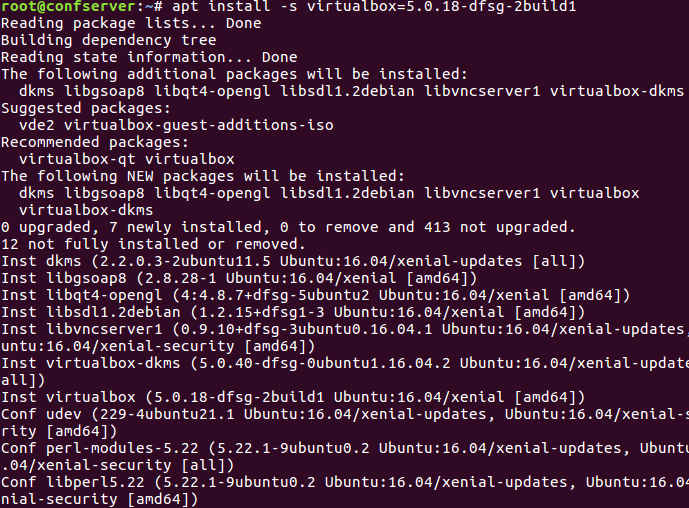
You can see that it shows the process of the installation but it is a just a simulation.
b. List the installed packages with the versions
You can need to check the version of an installed package. You can do it with the dpkg command combined with grep followed by the name of the package
sudo dpkg -l | grep virtualbox
ii unity-scope-virtualbox 0.1+13.10.20130723-0ubuntu1 all VirtualBox scope for Unity
ii virtualbox 5.0.18-dfsg-2build1 amd64 x86 virtualization solution - base binaries
ii virtualbox-dkms 5.0.40-dfsg-0ubuntu1.16.04.2 all x86 virtualization solution - kernel module sources for dkmsIf you want to filter the information, you can use the command as below
sudo dpkg -l | grep '^ii' | grep virtualbox | awk '{print $2 "\t" $3}'
unity-scope-virtualbox 0.1+13.10.20130723-0ubuntu1
virtualbox 5.0.18-dfsg-2build1
virtualbox-dkms 5.0.40-dfsg-0ubuntu1.16.04.2To list all the installed packages with version, you can use dpkg -l command.
Conclusion
It's not very often you come across a scenario to install specific package. Which specific package did you install recently and which method was used?
Thanks for reading, please leave your comment and suggestions in the below comment section.



Comments