1. Introduction
Your computer often gets updates, new programs, and logs that will obliviously consume disk space. You need to find how much space these objects consumed and act accordingly. The du command is used in Linux to calculate and display the disk usage of files and directories.
2. Syntax
The basic syntax of du command:
du [options] directories/filesThe following table shows the commonly used du command options:
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
| -h or --human-readable | Display disk usage in human-readable format (eg: KB, MB, GB...) |
| -s or --summarize | Display a summarised view of disk usage, only show the final total. |
| -S or --separate-dirs | Display disk usage excluding subdirectories. ie Specified directory and its immediate files. |
| -a | Display disk usage of all files and directories including hidden files. |
| -k | Disk usage in 1K block size. The default is 1024 bytes block size |
| -m | Disk usage in 1MB block size. |
| -B <block_size> | Set block size (eg -BM prints sizes in units of 1,048,576 bytes) |
| -t <threshold> | Display disk usage greater that the specified threshold |
| -c, --total | Display grand total size at the end of the output |
| --time | Display the last modification time along with disk usage. |
| ---exclude=<pattern> | Exclude files or directories that match a pattern from disk usage. |
| --exclude-from=FILE | Excludes files and directories listed in the mentioned file. |
| d or --max-depth=<depth> | Display disk usage in human-readable format (eg: KB, MB,GB...) |
| --help | Display usage information. |
3. Basic Usage of du command
Without any options, du command displays disk usage of the current directory and all its subdirectories. The output will include the disk space consumed by each individual directory.
du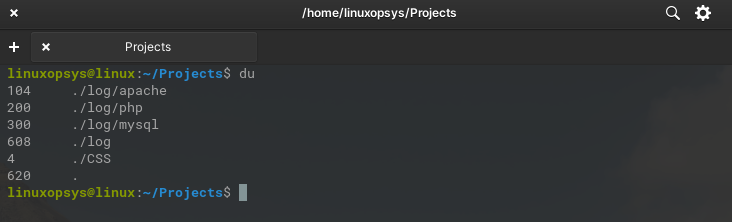
This lists disk usage of all directories except files. At the bottom line, it total size will include the size of files and directories.
Instead, you can display the usage of a directory
du /home/linuxopsys/projects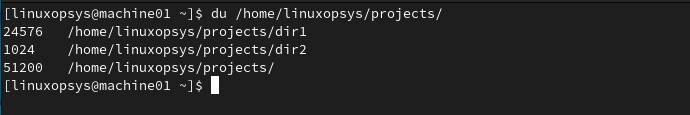
This lists disk usage of all directories and its subdirectories in /home/linuxopsys/projects. If you don't have appropriate permissions It won't list disk usage for those directories. You can use sudo with du command to avoid permission-denied messages.
You can exclude all "Permission denied" messages by appending 2> /dev/null to the command. This makes the output more neat.
Note: By default, du shows the size in 1024 bytes.
3. Exploring options of du command
Here are some commonly used options and examples of the du command:
3.1. Display in Human Readable Format [ -h option]
The default output of du command is not user-friendly. It would be easier to understand if it prints the sizes for example 1K, 25M, 2G, etc. Use -h oprion to print the size of the disk in a human-readable format.
du -h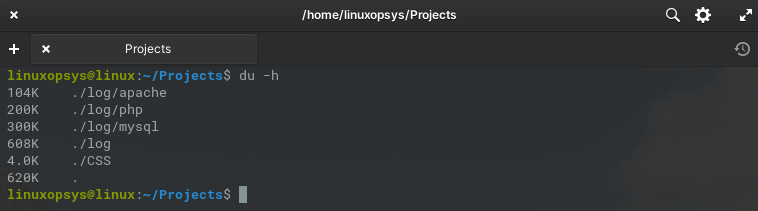
You may also use du -h * command to print user-friendly disk usage of all files and directories in the current directory and subdirectories.
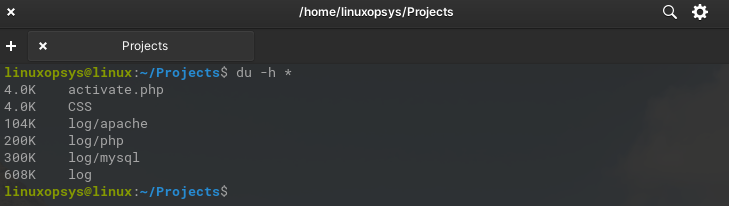
The du command also allows displaying disk usage from multiple directories by specifying the paths simultaneously. For example du -sh directory1 directory2 directory3
3.2. Summarize Disk Usage [-s option]
The -s option, also known as --summarize, is used to display only the total disk usage of each specified directory, suppressing the individual file and subdirectory details.
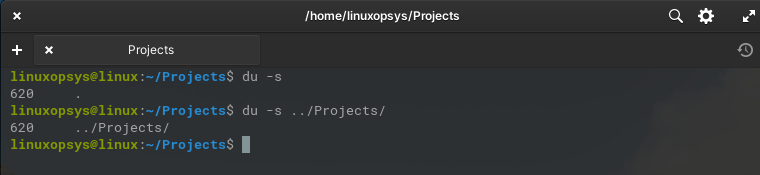
You may also du ../<directory-name> to print disk usage one level above. I love using -h option in conjunction for more readability.
The following command displays the final total disk usage ie a summary of the directory /home/linuxopsys/Projects in a human-readable format.
du -sh /home/linuxopsys/Projects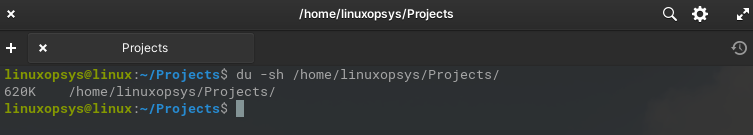
Whereas, du -sh * command can be used to display the summarized disk usage of all files and directories in the current directory. It provides a human-readable summary of the disk usage, showing the total size of each file and directory.
du -sh *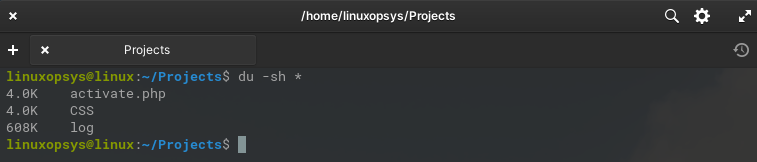
You may also use du -sh /path/to/file to display individual files size.
3.3. Display disk usage of all files and directories [-a option]
By default, du only displays the disk usage of directories, but with -a, it includes the sizes of individual files as well.
du -ah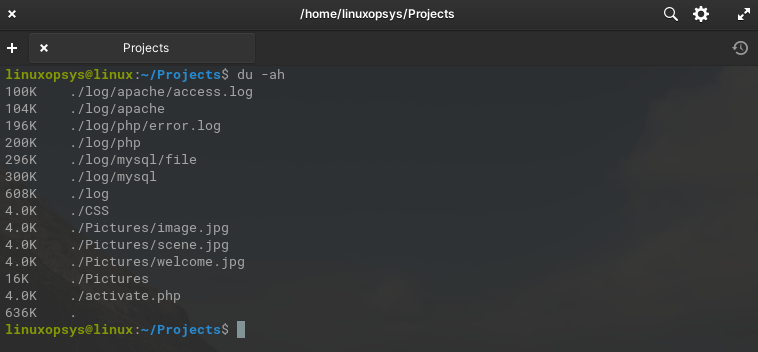
3.4. Display Directory disk usage in KB or MB units
Use -k with du command to display directory usage in Kilobytes:
du -k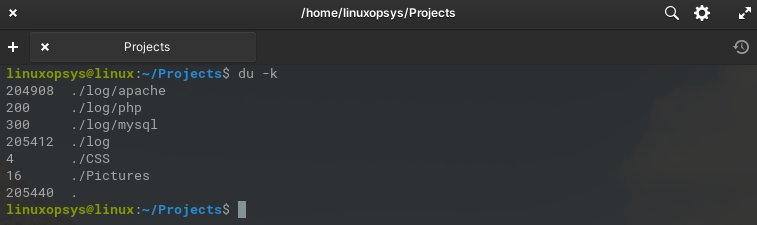
Use -m option with du command to display directory usage in megabytes:
du -m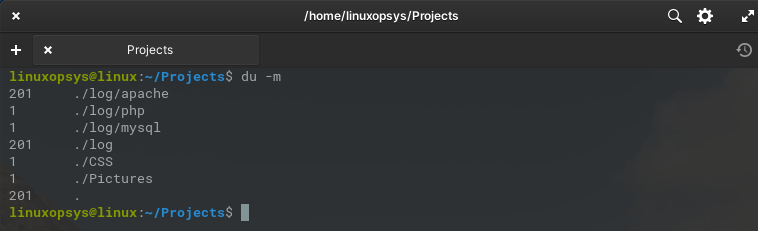
3.5. Display grand total size [-c option]
In the previous outputs, you might have seen the total usage at the bottom of the list. It's the same but the -c flag displays the text "total" showing the grand total disk usage for the specified directory or file.
Example:
du -ch Projects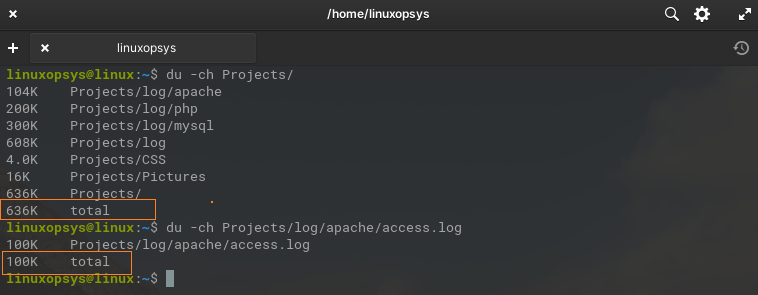
To find the total size of the specified files type use du -ch /directory-path/*.jpg command.
3.6. Display disk usage based on last modification time
Use --time option with du to display the last modification time of files or directories in addition to the disk usage information.
Example:
du -ah --time projects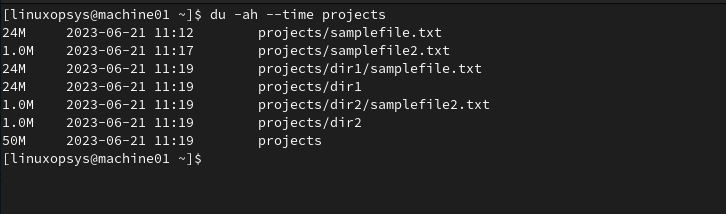
This list all files and directories in project directories with its size and last modification time.
Combining disk usage information with the last modification time provides enabling better analysis and decision-making.
3.7. Exclude
Use --exclude=pattern option with du command to exlcude specific patterns of files or directories from disk usage calculation.
Example:
The following command calculates the disk usage of the "Projects" directory, including all files and directories recursively, while excluding files with the ".jpg" extension.
du -ah --exclude="*.jpg" Projects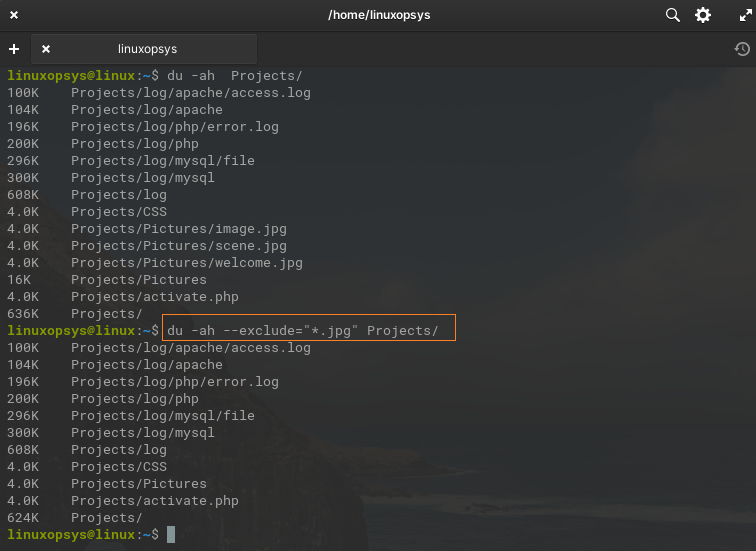
To exclude multiple directories from calculating the disk usage:
du -ah --exclude=path/to/directory1 --exclude=path/to/directory23.8. Display disk usage by directory one level
Use --max-depth=N with du to correct usage for limiting the depth of directory traversal.
For examples
du -h --max-depth=1 /home/linuxopsys/projects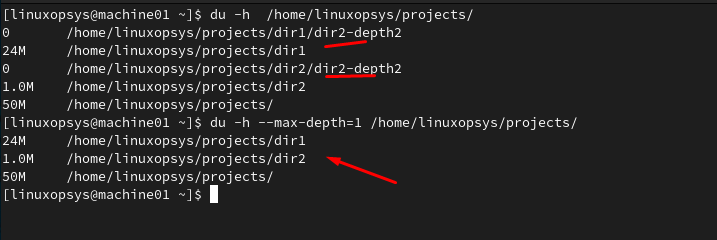
This will calculate the disk usage of the /home/linuxopsys/projects directory and its immediate subdirectories, limiting the depth to 1 level.
3.9. Filter by size
Use -t option with du command to specific size threshold. This make sure file and directories above the threshold will only be displayed.
du -ah -t 2MB /home/linuxopsys/projects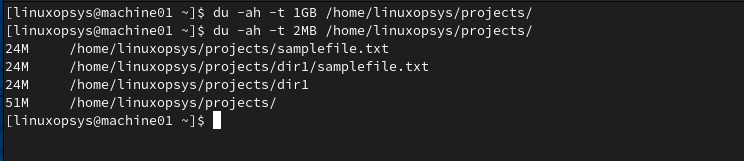
This displays files and directories above 2MB in size.
4. Sorting
Du command doesn't come with a sort option but we can combine it with other commands like sort to archive the desired sorting of disk usage.
By executing this command, you'll obtain a sorted list of the disk usage within the /home/linuxopsys/projects directory, with the smallest sizes appearing at the top.
du -ah /home/linuxopsys/projects | sort -h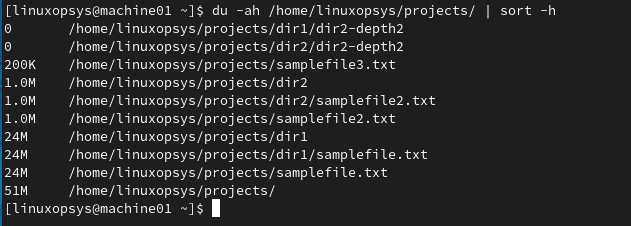
To sort the disk usage in descending order, you can add -r option to sort.
du -ah /home/linuxopsys/projects | sort -rh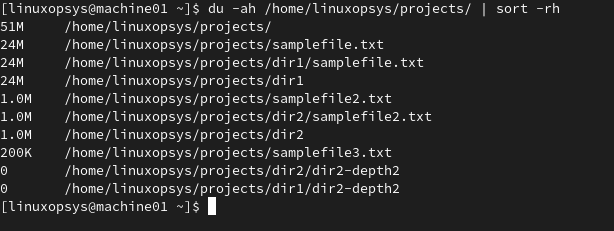
This helps to find the largest files and directories - the top line shows the largest file or directory.



Comments