You may need to delete the home directory if you no longer require the user's files and mails. In this tutorial, we learn how to delete a user and its home directory on a Ubuntu / Debian system.
1. See User Available
The /etc/passwd file contains a list of all users available on the system. You may use cat, less, awk, or cut commands to list the contents of the file.
For example, let's use cut command to extract the first field from the /etc/passwd file, ie only the username, type:
cut -d: -f1 /etc/passwdThis command will list all usernames in the Linux system.
To find the specific user you can use it with grep, as follows:
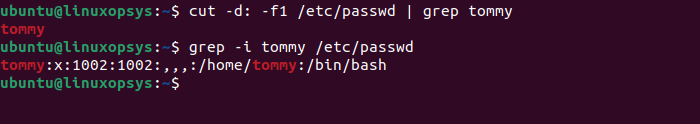
cut -d: -f1 /etc/passwd | grep tommyorgrep -i tommy /etc/passwd
2. Backup user Home Directory
To be safe, take a backup before deleting the user's home directory. You may use tar to create an archive file of user's home directory.
The following command creates a tar.gz file that contains the user tommy home directory.
tar -zcvpf /backup/tommy-backup-$(date +%d-%m-%Y).tar.gz /home/tommyOnce created, you can move the file to a backup media.
Here the syntax date +%d-%m-%Y adds the current date to the backup file name, so you'll know exactly when the backup was performed.
3. Delete user and its home directory
To prevent a user from any further access it's a good practice to block the user completely. For this, you can set the account to expire using chage command (example chage -E0 tommy). That even prevent even the user has any key authentication.
To prevent any errors, you may stop all processes associated with the user by running killall -u username command.
The recommended command to delete a user on Ubuntu is deluser. By default, the deluser <username> deletes the user but keeps its home directory.
To delete a user including the home directory use deluser with --remove-home option. Example
sudo deluser --remove-home tommy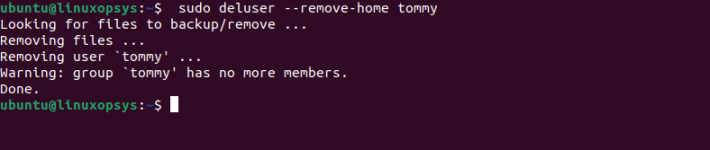
This command deletes the user named tommy and its home directory.
In case you need to delete all files owned by the user, use --remove-all-files option. This could impact the file owned by the user in any filesystem mounts. So, use it carefully.
4. Verify
You can verify the user has been deleted by using id command.
Example:
id tommy
The output "no such user" indicates that user tommy is not available on the system.
To verify that the user's home directory has been removed, use the command:
ls -la /home/tommy
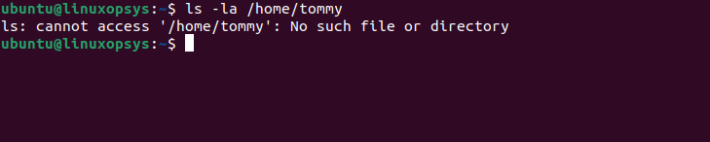
The output 'No such file or directory" indicates mentioned directory doesn't exist.
Conclusion
On Ubuntu and Debian systems, we can use deluser command to easily delete a user with the home directory.




Comments